Kidney Damage Is Silent, These 12 Early Signs Are Easy to Miss
Isha Gogia | Jul 13, 2025, 17:30 IST
Kidney damage silently progresses for years while disguising itself as common health complaints. From unexplained exhaustion to unusual urination patterns, these twelve critical warning signs appear long before obvious symptoms emerge. Recognizing these hidden indicators early can mean the difference between treatable kidney problems and irreversible organ failure requiring lifelong dialysis.
Human kidneys process substantial amounts of blood daily, maintaining chemical balance essential for survival. These fist-sized organs filter toxins, regulate blood pressure, produce vital hormones, and control fluid levels throughout the body. Despite their importance, kidney damage often progresses silently for years before becoming apparent.
The insidious nature of kidney disease lies in its ability to remain hidden until substantial damage has occurred. Unlike heart attacks or strokes that announce themselves dramatically, kidney deterioration whispers through subtle symptoms that most people dismiss as stress, aging, or minor health inconveniences. This silent progression allows the disease to advance unchecked, often reaching advanced stages before detection.
Medical professionals observe that many Americans live with chronic kidney disease, though the vast majority remain unaware of their condition. This widespread ignorance occurs because kidney damage symptoms frequently masquerade as minor ailments or aging effects. The body's remarkable ability to compensate for declining kidney function means that symptoms may not appear until kidney function has dropped to critically low levels.
Early warning signs often emerge years before kidney failure becomes obvious, presenting as seemingly unrelated health issues. Fatigue gets attributed to busy lifestyles, frequent urination blamed on coffee consumption, and swelling dismissed as temporary discomfort. This pattern of misinterpretation allows preventable kidney damage to progress toward irreversible stages. Understanding these warning signs becomes crucial for preventing irreversible organ failure and maintaining long-term health.
 Kidneys perform numerous essential functions beyond waste removal. They balance electrolytes, manufacture hormones controlling blood pressure, stimulate red blood cell production, and maintain proper acid-base levels. When kidney function deteriorates, these processes become compromised, creating cascading health problems throughout the body.
Kidneys perform numerous essential functions beyond waste removal. They balance electrolytes, manufacture hormones controlling blood pressure, stimulate red blood cell production, and maintain proper acid-base levels. When kidney function deteriorates, these processes become compromised, creating cascading health problems throughout the body.
Chronic kidney disease progresses through five distinct stages, from mild dysfunction to complete failure requiring dialysis or transplantation. Early detection during stages one or two allows interventions that may preserve remaining function and prevent complications.

Fluid Retention and Swelling Kidney damage disrupts normal fluid balance, causing swelling in characteristic locations. Early swelling typically appears around eyes, becoming particularly noticeable upon awakening. As damage progresses, swelling extends to ankles, feet, and legs.
This swelling, medically termed edema, occurs because damaged kidneys cannot efficiently remove excess fluid and sodium. The body retains water, causing tissue swelling. Unlike temporary swelling from prolonged standing, kidney-related edema persists and gradually worsens.


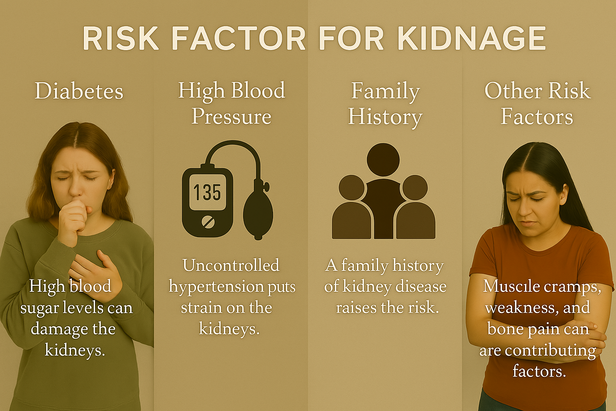
Certain medical conditions increase kidney damage risk significantly. Diabetes represents the leading cause, accounting for a substantial portion of kidney disease cases. Elevated blood sugar levels damage tiny blood vessels within kidneys, gradually reducing function.
High blood pressure ranks as the second leading cause, creating vicious cycles where kidney damage worsens blood pressure control. Family history plays crucial roles, as genetic factors influence kidney disease susceptibility.
Additional risk factors include autoimmune diseases, certain medications, recurrent kidney infections, and prolonged use of pain relievers. Age increases risk, with kidney function naturally declining over time.
 Specific symptom combinations warrant immediate medical evaluation. Blood in urine, regardless of quantity, needs prompt investigation. Sudden swelling, particularly facial swelling, may indicate rapidly progressing kidney damage.
Specific symptom combinations warrant immediate medical evaluation. Blood in urine, regardless of quantity, needs prompt investigation. Sudden swelling, particularly facial swelling, may indicate rapidly progressing kidney damage.
Severe fatigue interfering with daily activities, especially when combined with other symptoms, requires evaluation. Breathing difficulties, persistent nausea, or significant urination pattern changes demand immediate medical care.
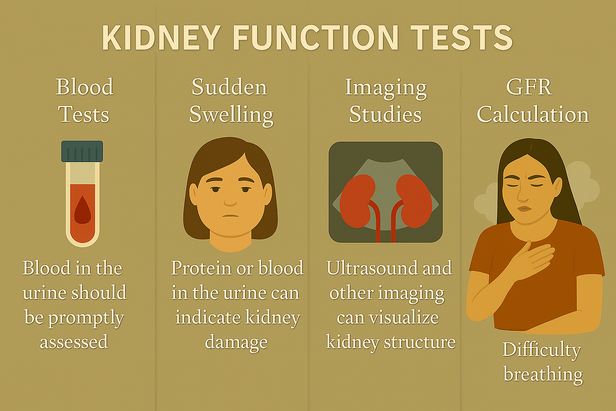
Medical evaluation typically begins with blood tests measuring creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels. These waste products accumulate when kidneys fail to filter properly. Estimated glomerular filtration rate calculations provide more accurate kidney function assessment.
Urine tests reveal protein levels, blood cells, and other abnormalities indicating kidney damage. Imaging studies like ultrasounds or CT scans visualize kidney structure and identify potential causes.
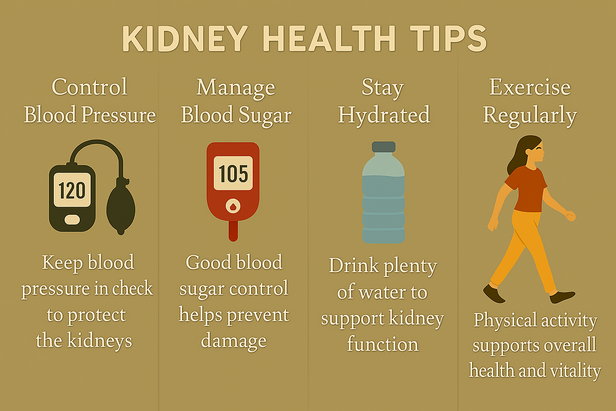
While some kidney damage proves irreversible, early intervention can significantly slow progression. Blood pressure and blood sugar control represent crucial prevention strategies. Regular monitoring helps detect problems before symptoms develop.
Lifestyle modifications including maintaining healthy weight, limiting sodium intake, staying properly hydrated, and avoiding excessive pain medication use protect kidney function. Regular exercise improves overall health and may help preserve kidney function.
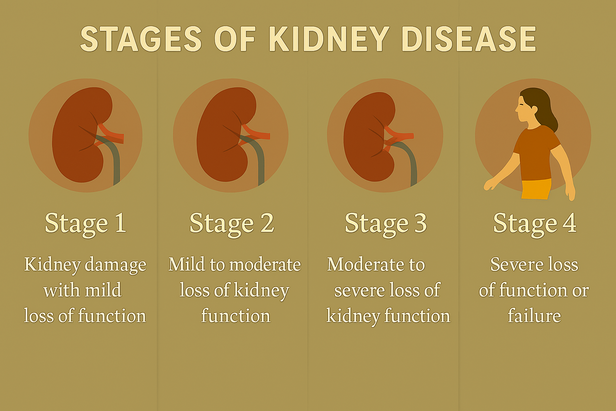
Kidney damage progression follows predictable stages, from mild dysfunction to complete failure requiring dialysis or transplantation. Early detection allows interventions that may preserve remaining function and prevent complications.
Unfortunately, kidney disease symptoms often remain subtle until damage becomes severe. This silent progression makes awareness of warning signs absolutely critical for preserving kidney health.
Your Kidneys Are Speaking - Are You Listening?
Recognizing kidney damage symptoms empowers individuals to seek timely medical care. While these symptoms may indicate other conditions, the potential for serious kidney disease makes evaluation essential.
Regular health screenings, particularly for high-risk individuals, can detect kidney problems before symptoms develop. Blood pressure monitoring, diabetes management, and routine laboratory tests provide early warning systems for kidney health.
Understanding these warning signs transforms passive health maintenance into active disease prevention. When kidneys send distress signals, careful observation and prompt response can preserve these vital organs for years to come. Early recognition and intervention remain the most powerful tools for maintaining kidney health and preventing devastating consequences of kidney failure.
Explore the latest trends and tips in Health & Fitness, Travel, Life Hacks, Fashion & Beauty, and Relationships at Times Life!
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
The insidious nature of kidney disease lies in its ability to remain hidden until substantial damage has occurred. Unlike heart attacks or strokes that announce themselves dramatically, kidney deterioration whispers through subtle symptoms that most people dismiss as stress, aging, or minor health inconveniences. This silent progression allows the disease to advance unchecked, often reaching advanced stages before detection.
Medical professionals observe that many Americans live with chronic kidney disease, though the vast majority remain unaware of their condition. This widespread ignorance occurs because kidney damage symptoms frequently masquerade as minor ailments or aging effects. The body's remarkable ability to compensate for declining kidney function means that symptoms may not appear until kidney function has dropped to critically low levels.
Early warning signs often emerge years before kidney failure becomes obvious, presenting as seemingly unrelated health issues. Fatigue gets attributed to busy lifestyles, frequent urination blamed on coffee consumption, and swelling dismissed as temporary discomfort. This pattern of misinterpretation allows preventable kidney damage to progress toward irreversible stages. Understanding these warning signs becomes crucial for preventing irreversible organ failure and maintaining long-term health.
Understanding Kidney Function

Kidney
( Image credit : Freepik )
Chronic kidney disease progresses through five distinct stages, from mild dysfunction to complete failure requiring dialysis or transplantation. Early detection during stages one or two allows interventions that may preserve remaining function and prevent complications.
Primary Warning Indicators

Lifeblood Cycle
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
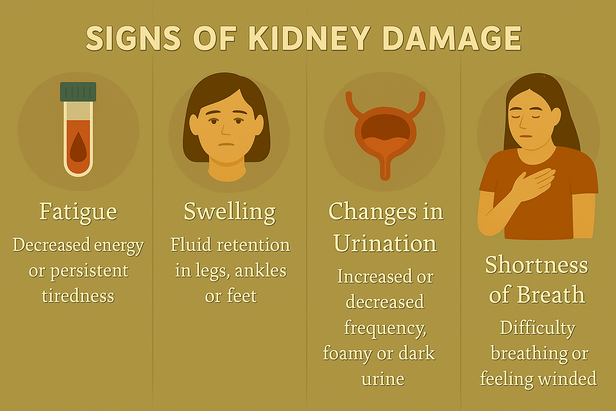
- Unexplained Fatigue and Exhaustion: Kidney damage frequently manifests as persistent tiredness that adequate rest cannot alleviate. As filtering capacity diminishes, waste products accumulate in blood, creating toxic conditions that drain energy reserves. Simultaneously, damaged kidneys produce insufficient erythropoietin, the hormone responsible for red blood cell creation, leading to anemia.This exhaustion differs markedly from ordinary tiredness. It persists despite proper sleep, intensifies with physical activity, and significantly impacts daily functioning. Many individuals attribute this symptom to stress or natural aging, allowing kidney deterioration to advance undetected.
- Urinary Pattern Changes: Kidneys regulate urine production, making urination alterations among the earliest damage indicators. Several distinct patterns emerge during kidney deterioration. Increased nighttime urination becomes particularly noticeable, with individuals waking multiple times nightly. Healthy kidneys concentrate urine during sleep hours, reducing nocturnal bathroom visits. Damaged kidneys lose this concentrating ability, producing dilute urine continuously.Foamy or bubbly urine indicates protein leakage, representing serious kidney damage. Healthy kidneys retain proteins within blood circulation, but compromised filters allow proteins to escape into urine. This creates persistent foam resembling beaten egg whites that lingers after flushing.
Fluid Retention and Swelling Kidney damage disrupts normal fluid balance, causing swelling in characteristic locations. Early swelling typically appears around eyes, becoming particularly noticeable upon awakening. As damage progresses, swelling extends to ankles, feet, and legs.
This swelling, medically termed edema, occurs because damaged kidneys cannot efficiently remove excess fluid and sodium. The body retains water, causing tissue swelling. Unlike temporary swelling from prolonged standing, kidney-related edema persists and gradually worsens.
Advancing Damage Symptoms

Vital Strain
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
- Respiratory Complications: Declining kidney function produces breathing difficulties through multiple mechanisms. Fluid retention affects lung function, causing shortness of breath during routine activities. Anemia from reduced red blood cell production decreases oxygen-carrying capacity, making simple tasks exhausting. Additionally, acid accumulation in blood forces lungs to work harder maintaining proper pH balance. This compensation mechanism eventually fails, leading to persistent breathing difficulties that worsen with physical exertion.
- Skin Manifestations: Kidney damage produces distinctive skin symptoms that many individuals overlook. Persistent itching, particularly during nighttime hours, occurs when kidneys cannot effectively remove phosphorus. Elevated phosphorus levels cause intense itching that topical treatments cannot relieve. Skin color changes also indicate kidney problems. Pale, yellowish skin suggests anemia development, while darker pigmentation may result from toxin accumulation. Some individuals notice metallic tastes in their mouth, caused by urea buildup in blood circulation.
- Cognitive Impairment: Brain function suffers when kidneys fail to remove toxins effectively. Early cognitive symptoms include concentration difficulties, memory problems, and mental fog. As damage progresses, confusion and disorientation may develop. These symptoms result from uremic toxins affecting brain function. Unlike age-related cognitive decline, kidney-related mental changes often fluctuate and may improve with appropriate treatment.
Advanced Warning Signs

Organ Strain
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
- Cardiovascular Impact: Kidney damage significantly affects heart health through multiple pathways. High blood pressure develops as kidneys struggle to regulate fluid balance and blood vessel function. This creates dangerous cycles where elevated blood pressure further damages kidneys. Irregular heartbeats may occur due to electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium and calcium disruptions. These rhythm disturbances can prove life-threatening without prompt medical intervention.
- Digestive Disturbances: Advanced kidney damage causes persistent nausea, vomiting, and appetite loss. These symptoms develop gradually as toxins accumulate in blood, affecting stomach function. Unlike temporary digestive illnesses, kidney-related digestive problems persist and worsen over time. Metallic taste accompanies these digestive symptoms, making food unappetizing and contributing to weight loss. Some individuals develop persistent hiccups that resist conventional treatments.
- Musculoskeletal Problems: Kidney damage disrupts mineral balance, causing muscle cramps, weakness, and bone pain. Calcium and phosphorus imbalances affect muscle function, leading to painful cramps particularly during nighttime hours. Bone pain develops as kidneys fail to activate vitamin D properly, affecting calcium absorption. This creates renal osteodystrophy, where bones become weak and painful.
Risk Factor Analysis

Genetic Strain
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
Certain medical conditions increase kidney damage risk significantly. Diabetes represents the leading cause, accounting for a substantial portion of kidney disease cases. Elevated blood sugar levels damage tiny blood vessels within kidneys, gradually reducing function.
High blood pressure ranks as the second leading cause, creating vicious cycles where kidney damage worsens blood pressure control. Family history plays crucial roles, as genetic factors influence kidney disease susceptibility.
Additional risk factors include autoimmune diseases, certain medications, recurrent kidney infections, and prolonged use of pain relievers. Age increases risk, with kidney function naturally declining over time.
Medical Attention Guidelines

Health Alert
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
Severe fatigue interfering with daily activities, especially when combined with other symptoms, requires evaluation. Breathing difficulties, persistent nausea, or significant urination pattern changes demand immediate medical care.
Diagnostic Procedures

Health Scan
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
Medical evaluation typically begins with blood tests measuring creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels. These waste products accumulate when kidneys fail to filter properly. Estimated glomerular filtration rate calculations provide more accurate kidney function assessment.
Urine tests reveal protein levels, blood cells, and other abnormalities indicating kidney damage. Imaging studies like ultrasounds or CT scans visualize kidney structure and identify potential causes.
Prevention Strategies

Healing Habits
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
While some kidney damage proves irreversible, early intervention can significantly slow progression. Blood pressure and blood sugar control represent crucial prevention strategies. Regular monitoring helps detect problems before symptoms develop.
Lifestyle modifications including maintaining healthy weight, limiting sodium intake, staying properly hydrated, and avoiding excessive pain medication use protect kidney function. Regular exercise improves overall health and may help preserve kidney function.
Detection Importance

Inner Balance
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
Kidney damage progression follows predictable stages, from mild dysfunction to complete failure requiring dialysis or transplantation. Early detection allows interventions that may preserve remaining function and prevent complications.
Unfortunately, kidney disease symptoms often remain subtle until damage becomes severe. This silent progression makes awareness of warning signs absolutely critical for preserving kidney health.
Your Kidneys Are Speaking - Are You Listening?

Health Pathway
( Image credit : Times Life Bureau )
Recognizing kidney damage symptoms empowers individuals to seek timely medical care. While these symptoms may indicate other conditions, the potential for serious kidney disease makes evaluation essential.
Regular health screenings, particularly for high-risk individuals, can detect kidney problems before symptoms develop. Blood pressure monitoring, diabetes management, and routine laboratory tests provide early warning systems for kidney health.
Understanding these warning signs transforms passive health maintenance into active disease prevention. When kidneys send distress signals, careful observation and prompt response can preserve these vital organs for years to come. Early recognition and intervention remain the most powerful tools for maintaining kidney health and preventing devastating consequences of kidney failure.
Explore the latest trends and tips in Health & Fitness, Travel, Life Hacks, Fashion & Beauty, and Relationships at Times Life!
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
- Can dehydration lead to kidney damage?Yes, chronic or severe dehydration can put a strain on your kidneys over time.
- Is there a specific diet recommended for kidney health?A balanced diet, low in processed foods, sodium, and excessive protein, generally supports kidney health.
- How often should I get my kidney function checked?Frequency depends on your risk factors, but regular check-ups are especially important if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of kidney disease.
